2 Characteristics and Influencing Factors of The Deep-sea Environment
2.1 Physical Characteristics of The Deep-sea Environment
The physical characteristics of the deep-sea environment include low water temperature, high water pressure, and scarce light exposure. Deep water is usually around 4 degrees Celsius, colder than surface water. This cryogenic environment challenges the survival of marine organisms, as the physiological activities of many organisms are affected by temperature.
At the same time, the water pressure in the deep sea is also another test for Marine life. For every 10 meters of increase in the water depth, the water pressure increases by one atmosphere, and the deep sea creatures need to adapt to the huge water pressure to survive. This high water pressure environment has an impact on the chemical reaction, nutrient transport and other aspects of the organism.
The scarcity of light in the deep-sea environment is also an important factor affecting marine life. Light cannot penetrate too deep in the deep sea, and most creatures have adapted to their dark environment, relying not on photosynthesis for energy, but in other ways to get food.
The physical characteristics of the deep-sea environment have a profound impact on the survival and reproduction of Marine life. Understanding the impact of the deep-sea environment on Marine life can help us to better protect the Marine biodiversity and maintain the Marine ecological balance [1].
2.2 Chemical Characteristics of The Deep-sea Environment
Figure 1: Chemical characteristics of the deep-sea environment
In the deep-sea environment, the oxygen concentration in the sea water is significantly reduced, and the oxygen content is lower than 0.5% of the sea level, leading to the weakened respiratory function of the deep-sea life. In addition, the high-pressure environment of the deep sea also has an important impact on Marine life. The pressure in the deep sea increases with increasing depth, leaving many marine organisms with unique physiological features, such as increased elastin, thickening of cell membranes, etc. The deep-sea environment also has the chemical characteristics of small temperature change, high salinity and unequal oxygen distribution, which have a certain influence on the life and reproduction of deep-sea organisms.
The chemical characteristics of the deep-sea environment not only influence the survival of marine organisms, but also have profound effects on their evolution and adaptation [2]. Understanding the chemical characteristics of the deep-sea environment is important for studying the ecological and evolutionary mechanisms of deep-sea organisms.
2.3 Biological Characteristics of The Deep-sea Environment
|
characteristic
|
description
|
|
acclimation
|
High pressure, low temperature, and the dark environment
|
|
growth characteristic
|
Slow growth, long life span, and huge body size
|
|
bioluminescence
|
Used for breeding, predation, and scaring of potential threats
|
|
Survival dependence
|
Special biochemical processes such as chemical synthesis and methane oxidation
|
Table 1: Biological characteristics of the deep-sea environment
The deep-sea environment is one of the most mysterious environments on Earth, filled with many unknown biological features. Deep-sea organisms adapt to extreme environmental conditions, such as high stress, low temperatures, and dark environments. This adaptability gives them unique characteristics, including slow growth, long life span, large body size, etc. In deep-sea environments, many organisms use bioluminescence to reproduce, predation and scare potential threats. Deep-sea organisms also rely on specialized biochemical processes for their survival, such as chemical synthesis and methane oxidation. The biological characteristics of the deep-sea environment are important for our understanding of marine biology and environmental conservation, and require further research and exploration.
3 Deep-sea Environment Simulation Methods
3.1 Overview of The Deep-sea Environment Simulation Equipment
In the paper "The Secret of the Deep Ocean: Modeling the Impact of the Deep-sea Environment on Marine Life", we will discuss an overview of the deep-sea environmental simulation equipment [3]. Deep-sea environment simulation devices are devices used to simulate factors such as pressure, temperature and light in the deep sea, which can help researchers better understand the survival of Marine life in extreme environments.
Among them, the deep sea pressure is a very important factor in the deep sea environment. Deep-sea organisms must adapt to extremely high pressures to survive in deep-sea environments. Deep-sea pressure can be expressed by the following mathematical formula:
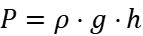
Among them, P stands for deep-sea pressure, ρ stands for water density, g stands for gravitational acceleration, and h stands for the depth of the deep sea. This formula can help us calculate the pressure suffered in different depths of the deep sea environment, so that we can better understand the living status of deep-sea creatures.
3.2 Deep Sea Environment Simulation
The deep sea environment simulation experimental method is an important means to help researchers better understand the impact of the deep sea environment on Marine life. Researchers will choose laboratory conditions that meet the characteristics of the deep-sea environment, such as temperature, pressure, and light control factors. Then, they will design a series of experiments, such as observing the growth and behavior of Marine organisms in different deep-sea environmental conditions.
Data acquisition is an indispensable step in simulation experiments of deep sea environment. Researchers collect data through various methods to truthfully monitor the growth rate, respiration and metabolic rate of Marine organisms. At the same time, they will also use advanced technologies, such as RNA sequencing and proteomics analysis, to obtain more accurate data.
The researchers will analyze the data, and use the statistical treatment of the experimental results to determine the influence law and mechanism of the deep-sea environment on Marine life. These research results can not only help us to better protect the deep-sea environment and Marine life, but also provide an important reference for human beings to use the deep-sea resources.
Overall, the importance of deep-sea environment simulation experimental method to reveal the impact of deep-sea environment on Marine life is obvious. Through these experiments, we can have a deeper understanding of the ability of deep-sea organisms to adapt to different environmental conditions, and provide a more reliable scientific basis for deep-sea biological research and conservation work.
4 Impact of The Deep-sea Environment on Marine Life
4.1 The Influence of The Deep-sea Environment on The Growth of Marine Life
Low water temperatures, scarce light, and low oxygen levels are all factors that influence the growth of marine life. Low temperatures can slow down the metabolism and growth rate of organisms, prolonging their growth cycle. Little light can also affect the photosynthesis of Marine plants, directly affecting the ecological process of the entire Marine ecosystem. Lower oxygen levels can limit the survival and growth of some Marine life.
The distribution of nutrients in deep-sea environments also plays a key role in the growth of marine life. Less nutrients in the deep-sea environment lead to the slow growth of low-level organisms in the food chain, which in turn affects the balance and stability of the entire Marine ecosystem. The population structure of marine organisms has changed dramatically in the deep-sea environment, with some adapted species predominant while other species are gradually declining.
Overall, the deep-sea environment has an important impact on the growth and reproduction of Marine life, which also makes the study of the deep-sea environment crucial. Only by deeply understanding the mechanism of the influence of the deep-sea environment on Marine life can we better protect the Marine ecosystem and maintain the diversity and ecological balance of Marine life [4]. The deep sea environment is not only a mysterious and challenging field, but also a valuable resource that we need to explore and protect.
4.2 The Metabolic Impact of The Deep-sea Environment on Marine Life
The effects of the deep-sea environment on marine life are very complex and subtle. In the deep-sea environment, oxygen levels are relatively low, especially in waters at depths of more than 1,000 m. This low oxygen environment can directly affect the energy metabolism process of Marine organisms. In low oxygen environment, the metabolic rate of Marine organisms will slow down, resulting in their growth and reproduction capacity.
In addition to the influence of oxygen content, the decomposition of organic matter is one of the important factors of the deep sea environment on the metabolism of marine organisms [5]. In the deep sea, the rate of decomposition of organic matter slows, which affects the feeding and energy conversion processes of Marine life. The ated decomposition of organic matter can also lead to food chain structure and energy loss different from shallow sea organisms.
The metabolic impact of the deep-sea environment on marine life embodies the complexity of energy conversion in deep-sea ecosystems [6]. Marine organisms adapt to survive in deep-sea environments, relying on the regulatory mechanisms of their metabolic rate and energy conversion. Therefore, the study of biological metabolism in the deep-sea environment is very important, which can help us to better understand the ecological adaptability and resource utilization strategies of deep-sea organisms, and provide a scientific basis for the protection of deep-sea ecosystems. The impact of deep-sea environment on Marine life is an important and worthy of in-depth research, and it is also one of the important directions of future research on Marine biology.
4.3 The Behavioral Influence of The Deep-sea Environment on Marine Life
The particularity of the deep-sea environment has an important influence on the behavior of marine organisms. In the deep sea environment, the light gradually weakens until it is completely disappeared, making many Marine organisms lose the ability to live and reproduce by the light [7]. Instead, some organisms have evolved other ways of sensing and guiding, such as smell, inductance, and stress sensing.
Water flows in deep sea environments also have effects on the migration and communication behavior of marine life. Changes in water flow affect the speed and direction of organisms, changing their habitat selection and food acquisition. Some migratory organisms use the direction of the water current to migrate long distances, while some fixed organisms are influenced by the water flow to grow and reproduce in suitable locations.
The deep-sea environment has a very important ecological impact on the behavior of Marine organisms. It not only directly affects the survival and reproduction of individual organisms, but also indirectly affects the balance and stability of the whole ecosystem. The particularity of the deep sea environment makes Marine organisms form a variety of unique survival strategies and behavior modes, and provide colorful topics and challenges for the research of Marine biology. Through in-depth study of the influence of deep-sea environment on marine biological behavior, we can better protect and manage Marine biological resources and promote the sustainable development of Marine ecological environment [8].
5 Conclusion
The deep-sea environment is a mysterious and wonderful field that is critical to the adaptive capacity and evolutionary mechanisms of marine organisms. The high pressure, low temperature, darkness and special chemical composition of the deep sea environment have a significant impact on the survival and living habits of Marine life. By simulating the deep-sea environment, we can better understand the survival strategies of Marine organisms in extreme conditions, and provide a scientific basis for the protection of Marine organisms and ecosystems. The deep-sea environment has a significant impact on the adaptability of Marine organisms, and the deep exploration of the survival strategies and mechanisms of Marine organisms in the deep-sea environment is expected to provide scientific basis and technical support for the protection of Marine organisms and the maintenance of Marine ecosystems [9]. The physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the deep-sea environment have a profound impact on the survival and reproduction of Marine life. Understanding the impact of the deep-sea environment on marine life is important for protecting marine biodiversity and maintaining marine ecological balance. The experimental method of deep sea environment simulation provides an important means to reveal the influence mechanism of deep sea environment on Marine life, and more accurate research results can be obtained through data collection and analysis. By studying the chemical characteristics, biological characteristics and behavioral characteristics of the deep-sea environment, the adaptive ability and resource utilization mode of deep-sea organisms can be better understood, and provide a more reliable scientific basis for the research and protection of deep-sea biology. The impact of the deep-sea environment on marine life is a complex and subtle area that requires further in-depth research and exploration. The deep-sea environmental simulation experimental methods provide an important means to reveal the importance of the impact of the deep-sea environment on Marine organisms. Studying the growth, metabolism, behavior and other aspects of Marine organisms can better understand the adaptability and ecological adaptability of deep-sea organisms to extreme environments [10]. The study of the deep-sea environment not only provides us with a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of Marine organisms and ecosystems, but also provides scientific basis and technical support for the protection and management of deep-sea ecosystems. Through in-depth research and exploration of the deep-sea environment, we can better protect and manage the Marine biological resources, and promote the sustainable development of the Marine ecological environment.

