2 Basic Knowledge of The Mechanism of Seed Dispersal
2.1 Definition of Seed Transmission
Seed dispersal is when plants disperse seeds to new geographical locations in order to reproduce. Seed dispersal is a very important link in the plant life cycle, enabling plants to adapt to different environments and expanding their distribution range.
Different plant seed transmission methods include wind transmission, animal transmission, water transmission and man-made transmission. Among them, wind transmission is suitable for light seeds, such as dandelion, which can be dispersed with the wind and spread to relatively distant places [3]. Animal transmission includes the excretion of animals after eating seeds, and the transmission of seeds attached to animals. For example, nuts are a typical example of achieving the purpose of reproduction through animal transmission.
Flow dispersal is suitable for aquatic plants whose seeds can float on the surface to new growth sites via flows of rivers or oceans. Man-made transmission refers to human intervention to bring seeds into new areas, such as sowing crops.
2.2 The Importance of Seed Transmission
Seed dispersal plays a crucial role in the plant life history. Seed dispersal not only contributes to the dispersal and reproduction of plant populations, but also promotes the diversity and stability of ecosystems. The transmission modes of different plant seeds also have their own characteristics. For example, wind-borne seeds can take root in distant places, while animal-borne seeds can often be brought to a suitable growth environment to germinate and grow.
A comparative study of the characteristics of different plant seed dispersal patterns may provide a better understanding of plant ecological adaptation strategies [4]. Some plants attract animals to spread their seeds through their fruits, not only protecting the seeds from wind and rain, but also using the animal activities to help with seed transmission. Some plants rely on the wind to spread the seeds through their light seed structure and strong endurance growth habits.
Overall, seed dispersal is diverse, unique and sophisticated, providing key support for plant survival and reproduction. Further studying the advantages and disadvantages of different plant seed dispersal mechanisms will help us to better protect and manage plant populations and maintain the health and stability of the ecosystem.
3 Classification and Description of Different Plant Seed Transmission Modes
3.1 Gravity Propagation
Gravity dispersal is an important way of seed dispersal, which mainly refers to the process of plant seeds spreading naturally under the action of gravity. This method includes direct landing, rolling and sliding, towing and other forms.
In direct ground dispersal, some seeds fall off from the plant by wind or other power, fall directly to the ground, and then spread by external factors (such as wind, water flow, etc.). In rolling glide dispersal, seeds roll forward on the ground, using the slope and smoothness of the terrain or the surface and the shape and characteristics of the seed itself to glide and spread to new places. Towing dispersal refers to the seeds attached to the hair or feet, and are taken to a new geographical location [5] as the animal moves.
3.2 Wind Power Transmission
Wind dispersal is a common form of plant seed dispersal, mainly through the power of the wind. In wind dispersal, the seeds are often light and appropriately winged, such as the flying seeds of a dandelion or the pine nuts in the pinecones. These special structures can allow the seeds to drift in the wind and spread over long distances.
Wind transmission is characterized by a wide range of applications, especially suitable for open areas or the lack of other means of transmission environment. For example, in desert or alpine areas, wind dispersal can help plant seeds reach new growth sites. Wind dispersal also improves the dispersal efficiency of seeds, allowing plants to more widely distribute and reproduce [6].
However, wind propagation also has some limitations. Due to wind instability, seeds may be scattered by the wind to inappropriate growth environment in the wind, leading to seed waste. The efficiency of wind dispersal is affected by the wind direction and wind force, and the distance and accuracy of seed dispersal will also be limited.
4 Empirical Method
4.1 Sample Collection
Sample collection is a crucial step in the comparative study of seed dispersal methods. We selected the appropriate time and method to collect seed samples from different plants according to the plant life cycle and reproductive characteristics. For wind dispersal plants, we collected scattered seeds around the plants with appropriate tools on sunny, breezy and windless days. For animal-borne plants, we set up cameras in the field to monitor and record how the animals carried and spread the seeds.
To ensure the reliability and accuracy of the experimental data, we strictly followed the standardized operation process during the collection process to ensure the integrity and representativeness of the samples. All the seed samples collected were carefully annotated and classified to ensure the accuracy of the subsequent experimental analysis. Through the rational use of these methods, we can obtain more objective and comprehensive research results, which can further reveal the wonders of different plant seed transmission methods.
4.2 Experimental Design
In this study, we will conduct a comparative study of different plant seed dispersal patterns to explore the wonderful journey [7] of seed dispersal. Experimental design is a key part that can ensure that our experimental results are reliable and valid.
In the experimental design, we need to consider the following factors:
1. Choose appropriate seed dispersal methods, such as wind, animal, or gravity [8].
2. Control for other variables that may affect the results, such as environmental factors and external interference.
3. Determine the number of replicates and the sample size of each experiment.
For the mathematical model in this study, we can use the following formula to describe the efficiency of seed dispersal:
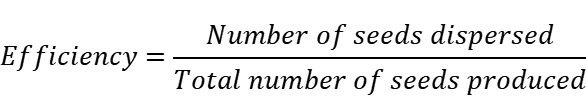
Where Efficiency represents the efficiency of seed dispersal, Number of seeds dispersed the number of seeds transmitted, and Total number of seeds produced the total number of seeds produced. This formula can help us to evaluate the effect of different seed dispersal modes and further compare the differences between them.
5 Experimental Results and Analysis
5.1 The Experimental Results of Gravity Propagation
Figure 1: Experimental results of seed dispersal distance and gravity dispersal
Seed dispersal is one of the key processes of plant reproduction, and the transmission modes of different plant seeds are also different. In this study, we compared three common seed dispersal methods [9], wind dispersal, animal dispersal, and gravity dispersal. The experimental results show that gravity dispersal has a unique advantage in terms of seed dispersal distance. Seeds of gravity dispersal are often able to complete dispersal over short distances rather than relying on external factors. This means that gravity dispersal is effective in helping plant seeds multiply in different environments. This finding will help us to have a deeper understanding of plant reproduction mechanisms and provide an important reference for protecting and promoting plant growth.
5.2 Experimental Results of Wind Power Propagation
|
Mode of plant seed dispersal
|
Use of wind transmission efficiency
|
Adaptive differences
|
|
Wing-like structure seeds
|
tall
|
low
|
|
Other seeds
|
low
|
tall
|
Table 1: Comparative experimental results of different seed transmission modes of plants
In the study, we present a detailed analysis of the experimental results on wind propagation. By observing the transmission mode of different plant seeds under wind force, we found some interesting phenomena [10]. Some plant seeds are more efficient in using wind transmission than other modes of transmission. For example, some seeds have special wing-like structure and can better use the power of wind for transmission. We also observed that some seeds differ in fitness during wind dispersal, with some being more susceptible to the external environment and others maintaining better in orientation and spread spread to the distances. Through the comparative analysis of the experimental results of different plant seeds during wind dispersal, we can learn more deeply about the differences in seed dispersal methods, and provide an important reference for further research.
6 Discussion and Outlook
6.1 Interpretation of The Experimental Results
The results of this experiment showed a significant difference in the effect of seed dispersal patterns in different plants. Comparative studies found that animal-borne seeds had a higher survival rate and dispersal range, while wind-borne seeds were more likely to cause locally dense distribution. This difference is mainly influenced by the seed characteristics and environmental factors.
Animal-borne seeds usually have nutrient-rich fruits, which bring the seeds to other sites for excretion, which facilitates the disperse populations and expands the distribution range. The seeds of wind transmission are light and easy to be dispersed by the wind, but they are also easy to gather in local areas, and it is difficult to form widespread distribution.
Environmental factors such as wind direction and topography can also affect the seed dispersal effect. In coastal areas or flat terrain, in mountainous areas or dense forests.
6.2 Future Research Direction
Future studies could deeply explore the adaptability of plant seed dispersal patterns in different environments, including the effects of climate change on seed dispersal and the interference of human activities with seed dispersal. And, meanwhile, the relationship between seed dispersal and biodiversity and the impact of seed dispersal on ecosystem stability can be investigated. Also, both genetic and evolutionary biology approaches can be combined to explore the relationship between seed dispersal and plant genetic variation.
There are also some shortcomings in this study, such as the small number of samples and the short study time, which affect the reliability and universality of the study conclusions. Therefore, we can increase the sample number and extend the study time to improve the scientificity and reliability of the study. A combination of field observation and laboratory experiments can be used to provide a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the mechanisms and characteristics of different plant seed transmission modes.
7 Conclusion
Based on the above studies, different plant seed transmission methods have their own characteristics and advantages. Wind transmission is suitable for light and small seeds, animal dispersal can bring higher survival rate and dispersal range, and gravity transmission has unique advantages in terms of dispersal distance. Through the comparative study of different transmission modes, we can better understand the transmission strategies and survival advantages of plants in different environments, reveal the evolution process of plant reproductive adaptability, and provide scientific basis for the protection of biodiversity and ecological balance. The study of seed dispersal mode provides valuable reference and inspiration for ecology, conservation biology and other fields, and promotes the rational utilization of natural resources and the sustainable development of ecosystems. By deeply exploring the wonderful journey of seed transmission, we can reveal the closely related ecological links between plants in nature, and provide scientific basis and theoretical support for the better protection and utilization of natural resources. Therefore, it is of great significance to compare different seed transmission modes of plants, which can help reveal the mysteries of plant biology and enrich our understanding of nature. Seed dispersal is of great significance for plant reproduction. The comparative study of different plant seed dispersal modes is the key to understand the plant ecosystem and reproduction mechanism, so as to provide scientific basis for biodiversity protection and ecological environment restoration.

