
Abstract:
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of different soil types on plant growth and to reveal the secrets of soil. Through the field investigation and the experimental data analysis, the different soil types showed significant differences in the provision of nutrients and water, which affected the plant growth and development. The pH, organic matter content and texture of soil play an important role in the root growth, uptake and utilization of nutrients. The diversity of microbial populations in different soil types also directly affects soil fertility and plant health. The results show that understanding the characteristics of soil and the effects of different types on plants can help develop planting strategies to improve soil fertility and plant growth efficiency. This study provides an important reference for deeply exploring the complex interaction relationship between soil and plants, which is important for promoting the sustainable development of agricultural production and ecological environment.
Keywords: soil, plant growth, nutrient cycle, microorganism, soil structure, sandy soil, loam, saline soil
1 Research Background
1.1 The Importance of Soil
Soils are an important basis for plant growth because they provide not only the nutrients needed for plant growth, but also the support and air needed for plant root growth. Nutrients in the soil, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential elements for normal plant growth and development, and they are taken up and converted into bioavailable forms through plant roots.
Microorganisms in the soil also play an important role in plant growth. Microorganisms in the soil include bacteria, fungi, and other microbial communities, which can promote the recycling and transformation of nutrients in the soil and form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, helping plants resist pests and diseases.
The structure of the soil is also essential for plant growth. The structure of soil affects the permeability and retention of oxygen, water and nutrients in the soil. Cohesating soil particles can increase the porosity of soil and improve soil aerability and water retention, thus facilitating the growth and development of plant roots.
Different types of soil also have different effects on plant growth. For example, sandy soil has good ventilation but poor water retention; clay soil has strong water retention ability but poor ventilation. Therefore, understanding the characteristics of different soil types could facilitate the rational selection of soil types of cultivated plants to promote plant growth and increase yield.
Soil plays an irreplaceable role in plant growth, and their nutrients, microorganisms and structures affect the growth and development of plants. Therefore, we should pay attention to the protection and improvement of soil to create a better growth environment for plant growth.
1.2 The Relationship Between Plant Growth and Soil
|
agrotype |
influence |
|
Sand soil |
It has a restrictive effect on plant growth, slow growth, dry leaves |
|
doras |
To promote the plant growth, the water and fertilizer performance is good, the plant growth is good, the leaves are green |
|
salt-affected soil |
Contains too much salt, cause adverse effects on plant growth, growth and development are blocked |
Table 1: Effect of different soil types on plant growth
In the process of studying the relationship between plant growth and soil, we found that different soil types have a significant impact on plant growth [1]. Through experimental observation and data analysis, we found that sandy soil has a significant restriction effect on plant growth. Sandy soils are highly permeable but have poor water and nutrient retention, leading to slow plant growth in this soil and dry leaves. In contrast, loam-type soils have a positive effect on plant growth. The loam has good water and fertilizer preservation performance, which provides sufficient water and nutrients for the plants, makes the plants grow well and the leaves are green. In contrast, saline soils containing too much salt can adversely affect plant growth [2]. Excessive salt will make it difficult for plants to absorb water and nutrients, which hinders plant growth and development. Therefore, according to the characteristics of different soil types, we can reasonably choose soil types to provide a good growth environment for plants, so as to maximize plant growth and development. Through in-depth research on the effects of different soil types on plant growth, it will help us to better understand the important factors of plant cultivation and provide a scientific basis for agricultural production [3].
2 Effects of Different Soil Types on Plant Growth
2.1 The Characteristics and Influence of Black Soil
When studying the effect of soil on plant growth, black soil is considered a very fertile soil type [4]. Its characteristics mainly include high content of organic substances, excellent water retention and permeability. These characteristics give black soil a significant promoting effect on plant growth. The high content of organic materials provides the nutrients needed by plants, and the water retention and permeability ensure that plant roots can get enough water and oxygen. Therefore, black soil is generally considered one of the ideal soil types for growing crops.
Mathematically, we can describe the influence of black soil characteristics on plant growth through the following formula:
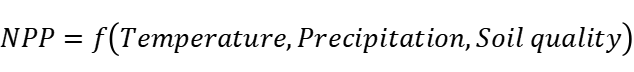
Specifically, NPP represents the net primary productivity of plants, Temperature and Precipitation represent temperature and precipitation, respectively, and Soil quality represents soil quality. This formula illustrates the positive effects of the high organic material content and good water retention and permeability on plant growth. By making rational use of these characteristics, we can better grow crops and improve the yield and quality of crops.
2.2 Characteristics and Influence of Red Soil
Figure 1: Effects of red soil on plant growth
Red soil is a special soil type that plays an important role in plant growth. Red soil has good water retention and air permeability, which enables plants to absorb water and oxygen smoothly, which is conducive to root growth and development. Red soil is rich in organic matter and minerals, which provides rich nutrients for plants, which is conducive to plant growth and nutrient absorption. The moderate PH value of red soil facilitates the growth of the vast majority of plants, especially for plants sensitive to PH.
Red soil also has a certain water retention, and can store a certain amount of water in the dry season, which is conducive to the growth and survival of plants under drought conditions. Red soil also has good thermal insulation, which helps to extend the growth cycle of plants and improve the yield and quality of plants.
Red soil has a positive impact on plant growth, and its characteristics include good water retention, air permeability, nutrient richness and moderate PH value, which provides a good soil environment for plant growth. Therefore, in the planting process, the rational use of red soil soil type, will help to improve the growth rate and yield of plants, and achieve better planting effect [5].
2.3 Characteristics and Effects of Sand and Soil
Sand soil is a soil type containing a high proportion of sand grains, its main characteristics are large soil grains and large particle gap, so strong permeability and good water permeability. This characteristic allows the roots to easily penetrate the soil and obtain oxygen, conducive to plant respiration. Sand can also drain the water quickly to avoid root decay caused by excessive soaking.
However, the water permeability and permeability of the sand also brought some negative effects. Due to the weak water retention capacity of sand soil, plants are susceptible to drought during growth. Especially in the dry season, sand is not enough to store enough water for plants to absorb, easily leading to dry plants or even death. Therefore, the drought resistance of plants should be considered when planting plants, and measures should be taken to increase the water retention of the soil, such as adding organic matter or covering topsoil for [6].
The lack of nutrients in the sand, mainly because of its large particles, it is difficult to absorb and store nutrients. Therefore, plants planted in sand usually need additional fertilizer to meet their needs for growth and development. Sand is also weak for plant roots, which is easy to lead to unstable plant growth and easy to be blown down by the wind.
The characteristics of sand and soil make it both beneficial and harmful in plant growth. When planting plants, according to the needs of the plants and the characteristics of the sand, reasonable fertilization, water conservation, and supporting measures should be taken to promote the good growth of the plants.
3 Effects of Soil Improvement on Plant Growth
3.1 The Role of Fertilization
Fertilization is a common method of soil improvement to increase the nutrient content in the soil and promote plant growth. Different types of fertilization have different effects on soil and plants. Organic fertilizer can improve the soil structure, increase the content of organic matter in the soil, improve the ability of soil water and fertilizer conservation, promote microbial activities, and contribute to plant growth. Inorganic fertilizer can quickly replenish the main nutrients needed by plants, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc., and improve the crop yield and quality of [7].
In addition to the type of fertilizer, the way it works can also affect plant growth. Excessive fertilization will lead to the accumulation of soil nutrients, resulting in soil pollution and affecting the balance of nutrient absorption by plants. Rational fertilization can improve the yield and quality of crops, and promote soil health and ecological balance. At the same time, according to the growth needs of different plants and soil types, it is also very important [8].
Plant nutrient absorption efficiency also varies in different types of soil. For example, in sandy soil, plant roots are easy to grow, but soil water and fertilizer retention ability is poor, so organic matter is needed to improve soil structure; in clay soil, plant roots are difficult to grow, but soil fertility is high, so plant growth efficiency can be improved through reasonable fertilization.
3.2 The Importance of Soil Conditioning
The effect of soil improvement on plant growth is evident. By adding organic substances, minerals and microorganisms to the soil, the soil structure and nutrient content can be improved, thus providing a better environment for plants to grow.
The structure of a soil plays a crucial role in plant root growth. Loose, breathable soil gives plants easier roots to grow down and better absorb water and nutrients. The soil is easier to form soil structure that is beneficial to plant growth, thus promoting root growth and development.
Nutrient content in the soil is also a key factor affecting plant growth. Appropriate addition of organic fertilizers and minerals can improve the content of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other nutrients in the soil to provide sufficient nutrients for plant growth. Nutrient-rich soil can promote plant growth and development and improve crop yield and quality.
The ized soil can also improve the water retention and ventilation of the soil, and avoid plant growth disorders caused by too wet or too dry soil. Through reasonable soil management and conditioning, it can create a conducive environment for plants, improve the resistance of plants to diseases and insect pests, and promote the healthy growth of plants.
3.3 The Influence of Soil Texture
Soil texture plays a crucial role in plant growth. Soils with different textures have different water retention abilities, which directly affect the growth of plants [9]. For example, sandy soil usually has good drainage ability, but its water retention ability is poor, which can easily lead to water shortage in plant roots. The clay soil is strong, but the drainage is poor, easy to cause root hypoxia.
Soils with different textures can also affect plant root growth. In sandy soil, roots often extend freely, which helps plants to absorb nutrients and water. However, in clay soil, roots are easy to be blocked, which affects the growth and development of plants. Therefore, it is very important to understand the texture characteristics of soil, select suitable soil and conduct soil improvement.
Soil improvement is a method to improve soil texture, which can improve the drainage and water retention ability of soil and create better conditions for plant growth. For example, adding an appropriate amount of organic material to the clay soil can improve the soil structure, improve the soil ventilation and water permeability, which is conducive to the growth of plant roots. The addition of some organic matter to the sandy soil can increase the fertility of the soil and help the plants to absorb nutrients.
Therefore, understanding the effect of soil texture on plant growth, selecting a suitable soil and performing soil improvement is crucial for [10]. Only by providing a suitable soil environment for plants can we ensure their healthy growth and harvest.
4 Conclusion
Soil is an important basis for plant growth, and its nutrients, microorganisms and structures all play an important role in plant growth and development. Different soil types have different effects on plant growth. Understanding the characteristics of different soil types helps to rationally select the soil types of cultivated plants to promote plant growth and increase yield. Fertilization and soil improvement are the key means to improve soil texture and nutrient content. Rational fertilization and soil improvement can improve soil structure and water retention ability, and provide a better growth environment for plants. By deeply studying the effects of different soil types on plant growth, it will help us to better understand the important factors of plant cultivation and provide a scientific basis for agricultural production. In the process of studying the relationship between plant growth and soil, we found that different soil types have significant effects on plant growth. Sandy soil has good permeability but poor water retention capacity; clay soil has strong water retention capacity but poor ventilation. Black soil has a high content of organic material, excellent water retention and permeability, and plays a positive role in promoting plant growth. Red soil has the characteristics of water retention, air permeability and moderate PH value, which is beneficial to the plant growth. Sand ventilation is good, but the water retention ability is poor, need to increase the water retention of soil. Fertilization is a common method of soil improvement, and the selection of appropriate fertilization method and fertilizer type have different effects on plant growth. Soil conditioning has an important impact on plant growth, and can improve the soil growth rate, yield and quality. Therefore, we should pay attention to the protection and improvement of soil to create a better growth environment for plant growth. Soil texture plays a crucial role in plant growth, with different textures having different water retention abilities and root growth characteristics. By adding organic material and making soil improvement, the soil structure and nutrient content can be improved to provide a better growth environment for plants. Soil conditioning and fertilization are of great significance for plant growth, and understanding the soil characteristics and taking appropriate measures can improve the plant growth rate and yield. May we work together to contribute to soil protection and plant growth.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author Contributions
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
The authors declared that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
